Ear Infections in Adults
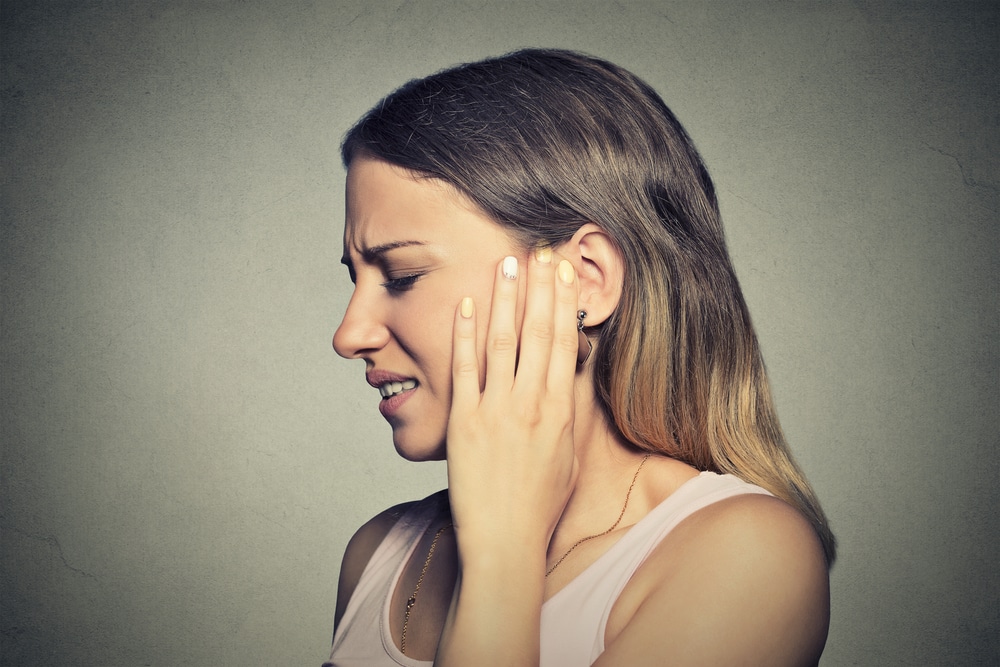

Although children are usually the ones afflicted by ear infections, adults can get them as well. Also known as otitis media, ear infections that affect adults are typically more serious than those that children get. Generally, adults who develop an ear infection should see an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) doctor for treatment. There are also preventative measures that can help prevent future ear infections.
Symptoms of an Adult Ear Infection
The middle ear is most commonly affected when an adult gets an ear infection. There are a number of symptoms that may be present if you have an ear infection. They include the following:
- Changes to your hearing
- Dizziness or vertigo
- Fever
- Headache
- Inflammation of the ear
- Nausea
- Pain in the ear
- Swelling of the ear
- Tenderness to the touch
- Vomiting
Causes and Risk Factors for Adult Ear Infections
Adults usually develop an ear infection as a result of a virus, bacteria, or even fungus. Individuals who have weakened immune systems and those who suffer from inflammation of the ear are more susceptible than generally healthy adults. Chronic health conditions like diabetes, eczema, psoriasis, or HIV can increase one’s risk for an ear infection.
When to See a Doctor
Some ear infections clear up on their own. However, others may be more difficult to get over, so if a person’s symptoms persist for longer than three days, it’s wise to see a doctor. Likewise, if new symptoms develop, it’s a sign that it’s time to see an ENT for treatment.
How is an Adult Ear Infection Diagnosed?
When you go in for a diagnosis, it’s important to inform the doctor of your full medical history and all symptoms you have experienced. You may also be asked about any medications you regularly take.
An ENT will then use an otoscope to examine the inside of your ear to check for an infection. When a diagnosis of ear infection is made, the doctor examines the eardrum and how it reacts to air pressure.
Treatment Options for Adult Ear Infections
A mild ear infection may clear up on its own while managing the symptoms. When the infection is more serious, there are a few treatment options available. The doctor may prescribe or recommend the following:
- Antibiotics: If the infection is bacterial, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics. However, whether antibiotics are needed depends on the severity of the infection.
- Prescription ear drops: The ENT may prescribe ear drops to treat the symptoms of an ear infection.
- Over-the-counter medications: The doctor may recommend that the patient take medications available over the counter, such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen, to treat the inflammation and pain of an ear infection.
Preventative Measures
Adults can take measures to prevent future ear infections. Changes to one’s lifestyle and improving personal hygiene can help. The following preventative measures can be taken:
- Quit smoking: Not smoking or quitting smoking can help to prevent ear infection and those that affect the upper respiratory tract.
- Proper cleaning and drying: It’s important to properly clean and dry the ears after bathing or swimming.
- Avoid cotton swabs: Avoiding cotton swabs to clean the ears is important as it makes it less likely to injure the ear canal or eardrum, which can result in an ear infection.
- Regular hand-washing: Adults should regularly wash their hands to avoid the spread of germs that can lead to an ear infection.
- Avoid allergy triggers: Those who have allergies should avoid triggers as often as possible and take allergy medication to reduce excess mucus that can lead to an infection.
Schedule a Consultation in Denver, Lone Tree & Castle Rock
If you are in Denver, Colorado and need to see an ENT for a possible ear infection, visit ENT Specialists of the Rockies and request an appointment with Dr. Nicolette Picerno, Dr. Christopher Cote, Dr. Jeffrey L. Cutler, Dr. Keith Swartz or Dr. Allison Rasband at your earliest convenience.
Associates of Otolaryngology, or, AOO | ENT Specialists of the Rockies has been serving multiple generations of families across the Denver Metro area since 1969. Our group of board-certified surgeons has been providing award-winning treatment and exceeding patients’ expectations with our specialized ENT services for over fifty-five years.
Thanks to our exceptional providers, we are an all-encompassing, comprehensive ENT practice. Our expert team of specialists includes general ENT surgeons, head and neck surgeons, sleep, sinus, and allergy specialists, and facial cosmetic and reconstructive surgeons. In addition, our team of providers is supported by doctoral-level audiologists, physician assistants, and nurse practitioners.