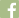
What are Tonsils and Adenoids?
Tonsils and adenoids are masses of tissue that are similar to the lymph nodes or “glands” found in the neck, groin, and armpits. Tonsils are the two masses on the back of the throat. Adenoids are high in the throat behind the nose and the roof of the mouth (soft palate) and are not visible through the mouth without special instruments.

Tonsils and adenoids are near the entrance to the breathing passages where they can catch incoming germs, which cause infections. They “sample” bacteria and viruses and can become infected themselves. Scientists believe they work as part of the body’s immune system by filtering germs that attempt to invade the body, and that they help to develop antibodies to germs.
This happens primarily during the first few years of life, becoming less important as we get older. Children who must have their tonsils and adenoids removed suffer no loss in their resistance.
What Affects Tonsils And Adenoids?
The most common problems affecting the tonsils and adenoids are recurrent infections (throat or ear) and significant enlargement or obstruction that causes breathing and swallowing problems.
Abscesses around the tonsils, chronic tonsillitis, and infections of small pockets within the tonsils that produce foul-smelling, cheese-like formations can also affect the tonsils and adenoids, making them sore and swollen. Tumors are rare but can grow on the tonsils.
What Patients Are Saying
Everyone was friendly, professional and respectful. I was made to feel comfortable and confident in the Doctor and her assistant. I feel that I am in good hands with Dr. Rasband.
I had a severely obstructive scar tissue band removed from my right nasal cavity as well as a turbinate reduction. My surgery with Dr. Rasband was 1 month ago and I am LOVING the outcome! Just a few days after surgery, I was breathing 100% better. Dr. Rasband provided me with some cool pictures of the surgery. Recovery was quite easy, I was actually able to attend a work meeting the next day in office. I saw her a few times since then for post-op appointments. No re-adherence of the scar tissue band, and I am breathing 100% better. It’s amazing to have both sides of my nose open!
Write A Review
When Should I See My Doctor?
You should see your doctor when you or your child suffer the common symptoms of infected or enlarged tonsils or adenoids.
Your Examination
The primary methods used to check tonsils and adenoids are:
- Medical history
- Physical examination
- Throat cultures/Strep tests
- X-rays
- Blood tests
What Should I Expect At the Exam?
Your physician will ask about problems of the ear, nose, and throat and examine the head and neck. He or she will use a small mirror or a flexible lighted instrument to see these areas. Cultures/strep tests are important in diagnosing certain infections in the throat, especially “strep” throat.
Tonsil and Adenoid Diseases Treatments
Bacterial infections of the tonsils, especially those caused by streptococcus, are first treated with antibiotics. Sometimes, removal of the tonsils and/or adenoids may be recommended. The two primary reasons for tonsil and/or adenoid removal are (1) recurrent infection despite antibiotic therapy and (2) difficulty breathing due to enlarged tonsils and/or adenoids.
Such obstruction to breathing causes snoring and disturbed sleep that leads to daytime sleepiness in adults and behavioral problems in children. Some orthodontists believe chronic mouth breathing from large tonsils and adenoids causes malformations of the face and improper alignment of the teeth.
Chronic infection can affect other areas such as the Eustachian Tube – the passage between the back of the nose and the inside of the ear. This can lead to frequent ear infections and potential hearing loss.
Recent studies indicate adenoidectomy may be a beneficial treatment for some children with chronic earaches accompanied by fluid in the middle ear (otitis media with effusion).
In adults, the possibility of cancer or a tumor may be another reason for removing the tonsils and adenoids.
Tonsillitis Symptoms
Tonsillitis is an infection of one or both tonsils. One sign is swelling of the tonsils. Other signs or symptoms are:
- Redder than normal tonsils
- A white or yellow coating on the tonsils
- A slight voice change due to swelling
- Sore throat
- Uncomfortable or painful swallowing
- Swollen lymph nodes (glands) in the neck
- Fever
- Bad breath
Enlarged Adenoids And Their Symptoms
If you or your child’s adenoids are enlarged, it may be hard to breathe through the nose.
Other signs of constant enlargement are:
- Breathing through the mouth instead of the nose most of the time
- Nose sounds “blocked” when the person speaks
- Noisy breathing during the day
- Recurrent ear infections
- Snoring at night
- Breathing stops for a few seconds at night during snoring or loud breathing (sleep apnea)
Frequently Asked Questions
Are adenoids removed with tonsils?
Adenoids are generally not removed with adult tonsillectomy, as they shrink with age. They are often removed with the tonsils in pediatric patients if large and contributing to nasal obstruction or if chronically infected.
Can enlarged adenoids cause Behavioural problems?
A 2012 article from the Journal, Pediatrics, reports that sleep-related breathing problems due to obstructive adenoids may increase the chances that a child may develop behavioral problems.
Can homeopathy cure adenoids?
Homeopathy cannot cure enlarged adenoids; ultimately, obstructive adenoids need surgical removal.
Do adenoids grow back?
Yes, but this is rare and occurs if not all the adenoid tissue is removed. The residual tissue can rarely regenerate or become enlarged during an acute infection.
Do tonsils affect sleep?
If large enough, the tonsils can obstruct the airway and contribute to sleep apnea.
Does removing your tonsils affect your immune system?
No. The lingual tonsils, located at the back of the tongue, help to fight infection in the absence of the tonsils.
How can I shrink my adenoids naturally?
There is no real way to shrink the adenoids naturally.
How do adenoids get infected?
Adenoids are lymphatic tissue and help fight infection by collecting bacteria and viruses. This is also the same manner in which they can become infected.
How do doctors check adenoids?
The adenoids are visualized via an endoscopy in the nasopharynx.
How do doctors remove adenoids?
The adenoids are generally removed via coblation.
How long does a child stay in hospital after having tonsils out?
Most tonsillectomy procedures are outpatient and do not require a hospital stay.
Is lemon good for tonsils?
Citrus products can aggravate and causing burning if the tonsils are already painful and irritated.
What causes enlarged tonsils and adenoids?
Enlarged tonsils and adenoids can be due to chronic infection or they may be this way simply due to someones anatomy.
What do swollen tonsils look like in a child?
The tonsils will appear large and likely inflamed/red.
Why removing tonsils is bad?
A tonsillectomy is not bad; however, there are risks associated with the surgery like any other surgery. The biggest risk is bleeding.
Why you shouldnt remove your tonsils?
The tonsils should not be removed if you do not meet the clinical criteria from a tonsillectomy.
Can adenoids affect sleep?
Large adenoids can contribute to obstructive sleep apnea.
Can xray show adenoids?
No. Adenoids are not visualize on x-ray, but they are visualized on a CT scan of the neck.
Can you die from tonsillectomy?
Yes; however, a tonsillectomy carries a low risk of morbidity and mortality. The rate of tonsillectomy morality is 1 death per every 20.000 procedures.
Can you see adenoids through mouth?
No. The adenoids are in the nasopharyx. This region of the body is where the back of the nose turns down to meet the throat.
Do adenoids affect speech?
Yes. Enlarged adenoids can affect the resonance of speech, thus affecting a childs intelligibility.
Do adenoids cause post nasal drip?
Adenoids do not cause post-nasal drip.
Do adenoids go away with age?
Adenoids begin to shrink after age five and are nearly gone by the teenage years
At what age do adenoids shrink?
Adenoids begin to shrink after age five and are nearly gone by the teenage years.
Can removing tonsils cause cancer?
Can you live without tonsils?
Yes. You do not need your tonsils. There are no adverse consequences to not having tonsils.
Can your tonsils grow back?
Yes, but this is rare and occurs if not all the tonsil tissue is removed. The residual tissue can rarely regenerate or become enlarged during an acute infection.
How can I permanently cure my tonsils?
Tonsillectomy (surgical removal).
How do you get rid of sore tonsils?
If infected, sore tonsils can be treated by treating the infection with antibiotics and/or steroids. If severe enough, tonsillectomy is performed.
Is adenoid surgery painful?
Most people experience pain after an adenoidectomy; however, the pain is well controlled with prescription pain medication or even Tylenol.
Is milk good for tonsillitis?
Dairy can thicken or increase mucus production and therefore, may not be helpful in tonsillitis.
Is tonsillectomy a major surgery?
Tonsillectomy is a major surgery, but is outpatient surgery and is generally tolerated well.
What are the side effects of having your adenoids removed?
The biggest risk associated with adenoidectomy is bleeding.
What foods to avoid if you have adenoids?
Do you get sick more without tonsils?
You do not get sick more without tonsils. In fact, you may will likely get sick less if the tonsils were removed for chronic tonsillitis.
Does removing adenoids help with sleep apnea?
It the adenoids are large enough to obstruct the airway, an adenoidectomy can help with sleep apnea.
Does your voice change after tonsillectomy?
Tonsillectomy can change the resonance of your voice, but this is rare and mild.
How do they test for tonsil cancer?
A biopsy of the tonsil can be performed and sent to pathology or the tonsils can be removed completely and sent for pathology.
How long can swollen tonsils last?
This can vary. Generally, the tonsils will be swollen as long as the infection is present.
How long does an adenoid surgery take?
The surgery itself takes about 30 minutes to one hour.
Is it OK to cough after a tonsillectomy?
What is best medicine for tonsils?
This depends on the cause of the infection: bacterial vs. viral and what type of bacteria.
Can adenoids be treated without surgery?
Acute flares of adenoiditis can be treated with medication; however, obstructive adenoids generally need surgical removal.
Can adults have adenoids removed?
If the adenoids are still present and problematic, adults can have an adenoidectomy.
Can dentist remove tonsil stones?
Dentists and otolaryngologists can remove tonsil stones with an air or water syringe. Tonsil stones can also be manually extracted.
How do you know if you need adenoids removed?
Adenoidectomy is needed if the adenoids are chronically infected or enlarged and causing airway obstruction.
How do you know if your child needs tonsils out?
Tonsillectomy is needed if the tonsils are chronically infected or enlarged and causing airway obstruction.
What are adenoids and why remove them?
Adenoids are lymphatic tissue located in the nasopharynx. They help to fight infection. Removal is needed when they are chronically infected or enlarged and obstructing the airway.
What can adults eat after tonsillectomy?
Liquid and soft foods can be eaten after tonsillectomy.
What does adenoids do for the body?
Adenoids help fight infection.
What happens after a 3 year old tonsillectomy?
Children generally recover well and quickly after a tonsillectomy and generally do not need more than OTC medication for pain.
What is the best treatment for adenoids?
The most definitive way to treat chronically infected or enlarged adenoids is an adenoidectomy.
When should a childs tonsils be removed?
A childs tonsils should be removed when they become chronically infected or enlarged, causing airway obstruction.
Why do they not remove tonsils anymore?
Tonsils are still removed, but only if the proper indications are met. Tonsils are simply not removed just for the sake of removing them.
Why is a tonsillectomy more dangerous for adults?
A tonsillectomy is not necessarily more dangerous for adults; however, adults do have a more painful and longer recovery than children.
Is Your Sore Throat a Cold, Strep Throat, or Tonsillitis?
READ BLOG